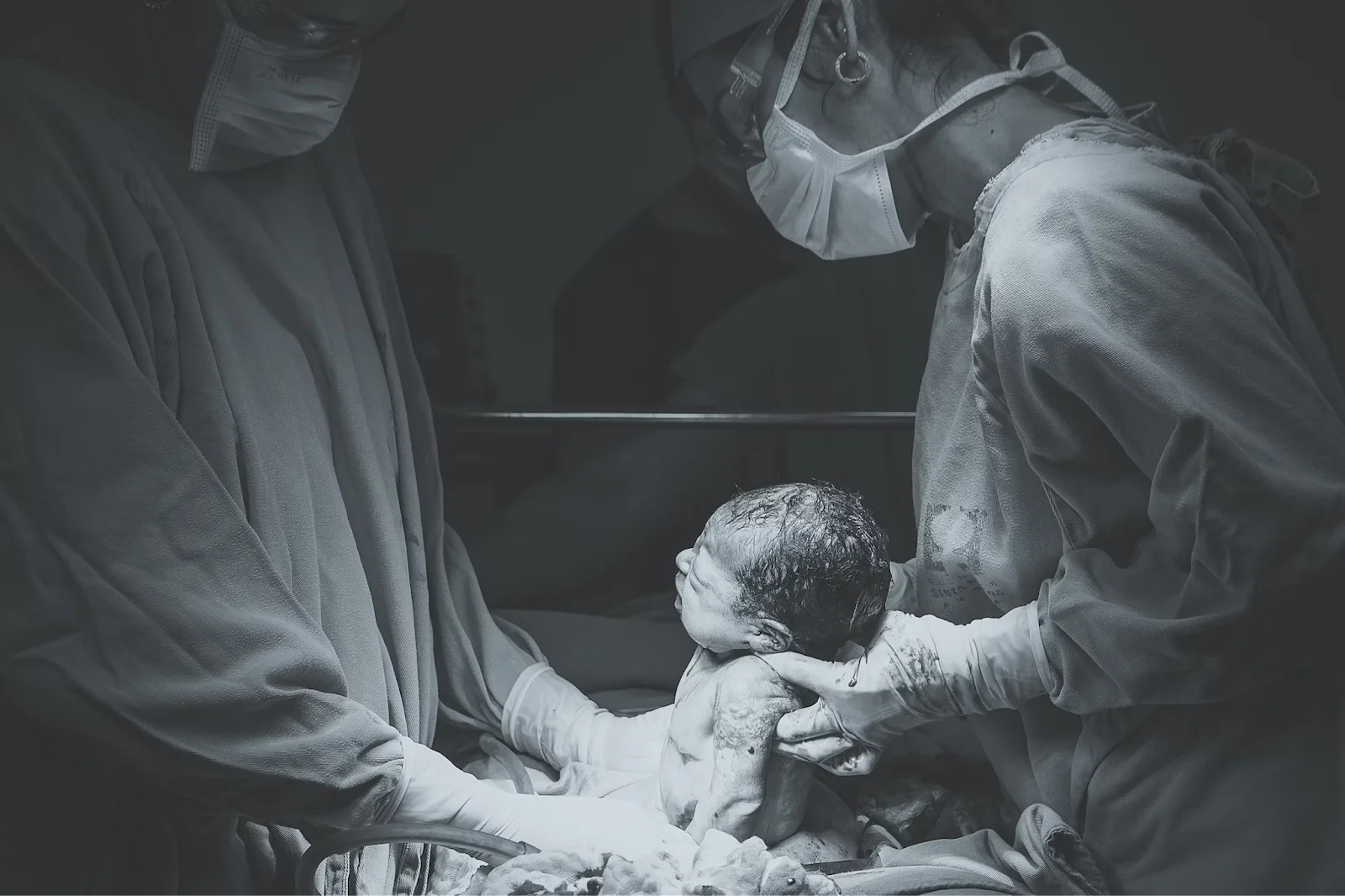
A child’s birth is a joyous and transformative moment in the parents’ lives. But childbirth can also present various challenges, and occasionally, birth injuries occur. These injuries, known as birth trauma, can range from mild to severe, impacting both the baby and the family.
Head injuries are the most common among the various types of birth trauma. So, if you believe your child has suffered a birth injury due to negligence, it’s important to consult with experienced birth injury lawyers.
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and potential long-term effects of head injuries during childbirth.
The Most Common Birth Trauma: Head Injury
Head injury refers to trauma that affects the baby’s skull, scalp, or brain during birthing. According to the Merck Manual, head injuries occur when external forces exert pressure on the baby’s head as they pass through the birth canal. The pressure can result in various injuries, such as skull fractures, scalp lacerations, or brain damage.
Causes of Head Injuries During Birth
Several factors contribute to the occurrence of head injuries during childbirth. The most common causes include:
- Prolonged Labor: When labor is excessively long, the prolonged pressure on the baby’s head can lead to head injuries.
- Challenging Presentation: If the baby is positioned abnormally during birth, such as a breech position (buttocks or feet first), it can increase the risk of head trauma.
- Large Baby Size: Babies with above-average birth weight may have a higher risk of experiencing head injuries due to the increased difficulty navigating the birth canal.
- Assisted Delivery: Using forceps or vacuum extractors during delivery can increase the likelihood of head injuries if not used properly.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Babies with brain injuries may show various signs and symptoms according to the extent of the damage. Common indicators may include:
- Swelling or bruising on the scalp
- Scalp lacerations or abrasions
- Abnormal head shape
- Persistent crying or irritability
- Difficulty feeding
- Excessive sleepiness or lethargy
- Seizures
Medical professionals perform a thorough physical examination when a head injury is suspected. They may order additional diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, to assess the extent of the injury and any potential brain damage.
Long-Term Effects and Treatment
The long-term effects of head injuries during birth can vary widely, ranging from temporary discomfort to severe and permanent disabilities. Immediate medical intervention is crucial in minimizing potential complications.
Treatment options for head injuries may include:
- Observation: Mild head injuries often require only close observation to ensure symptoms do not worsen.
- Pain Management: To help ease any pain or suffering caused by the injury, a doctor may recommend taking certain medications.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases of skull fractures or brain damage, surgery may be necessary to repair or stabilize the affected area.
- Rehabilitation: Babies who experience brain damage may require long-term rehabilitation to address developmental delays, motor impairments, or cognitive challenges.
Prevention and Intervention
While birth injuries, including head trauma, cannot always be prevented, specific measures can reduce the risk and mitigate potential complications. Regular prenatal care, close monitoring during labor, and skilled obstetric management are crucial in ensuring the best possible results for both mother and baby.
Furthermore, healthcare professionals should receive adequate training in using delivery-assisting tools, such as forceps and vacuum extractors, to minimize the risk of injury. Prompt and accurate diagnosis of head injuries is essential for timely intervention and management.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, head injuries are the most common form of birth trauma, resulting from external forces applied to the baby’s head during delivery. Preventive measures, such as prenatal care and skilled obstetric management, are essential in minimizing their occurrence.
Prompt recognition, accurate diagnosis, and timely intervention are crucial for optimal outcomes. Comprehensive support and access to specialized medical professionals are vital for families affected by birth trauma.
By prioritizing prevention, early intervention, and support, we can strive to minimize birth trauma and provide comprehensive care for newborns and their families.