Tungsten metal, a renowned compound known for its outstanding hardness, high melting point, and wide range of applications, is an enthralling element that plays an important role in a variety of sectors and industries globally. But have you ever wondered how tungsten is made? Let’s jump in and explore the intricate process of producing tungsten metal, shedding light on the path from ore to finished tungsten product.
Tungsten Ore Extraction
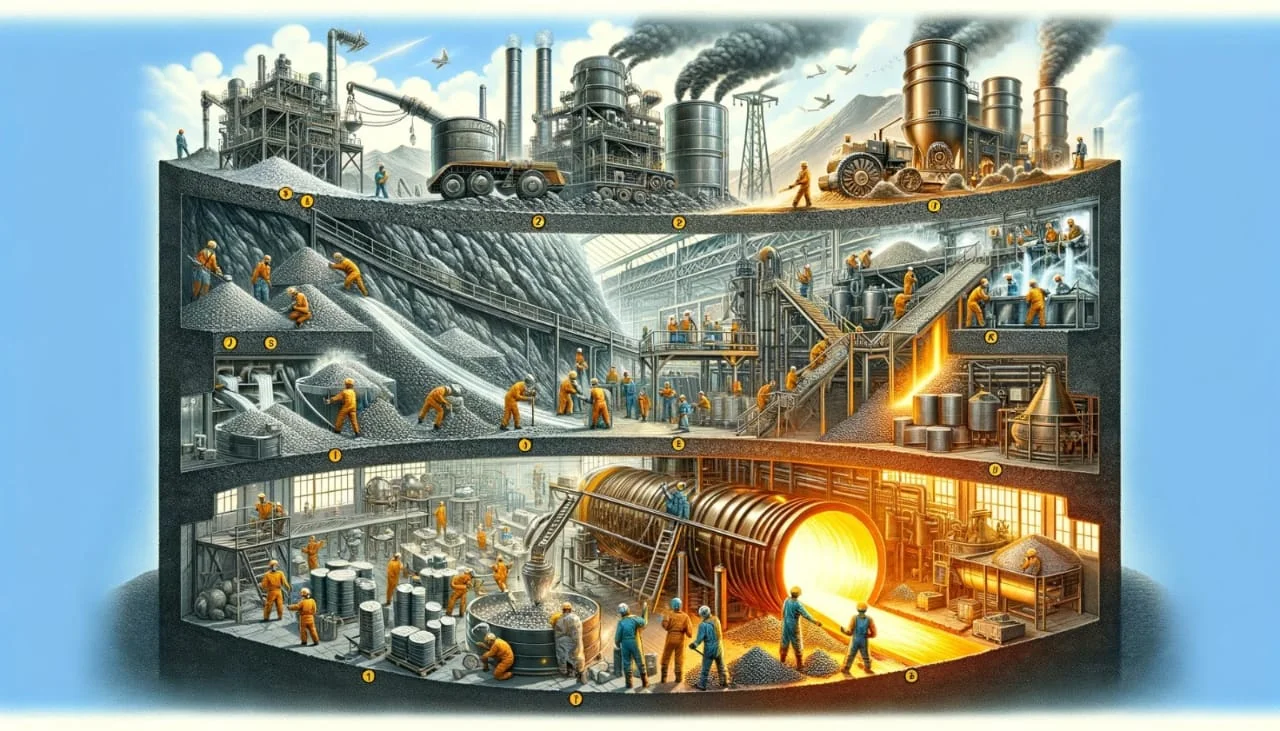
Tungsten metal is not found in nature in its pure form; instead, it’s extracted from tungsten ore minerals. Wolframite and scheelite are the principal sources of tungsten metal. Tungsten is commonly found in these types of tungstate minerals. Mining, crushing, and then concentrating these ores to produce a concentrate with a high tungsten metal content is how this highly sought-after critical mineral is extracted.
Tungsten Oxide Production
The conversion of tungsten concentrate into tungsten oxide is the next step in tungsten metal’s journey. This procedure often involves roasting the concentrate in the presence of air. As a result, tungsten concentrate is converted into tungsten metal trioxide (WO3), a yellowish substance that is a critical intermediate in the synthesis of tungsten metal.
Tungsten Powder Reduction
A reduction technique is used to get pure tungsten metal from tungsten oxide. The reduction is often accomplished through the use of hydrogen or carbon, resulting in the creation of tungsten powder. This fine powder serves as the starting point for the production of numerous tungsten metal products.
Ferrotungsten: An Alloy for Improved Tungsten Metal Properties
In some applications, tungsten metal is alloyed with iron to form ferrotungsten, a strong tungsten metal alloy notable for its magnetic characteristics. Ferrotungsten is created by fusing tungsten powder with iron in an electric arc furnace (EAF). The furnace creates the formation of an electric arc between three vertical graphite electrodes to produce temperatures in excess of 3000 degrees Celsius. This high temperature melts the raw materials, allowing for metallurgical reactions that result in the creation of molten ferrotungsten. To provide high-quality outputs, the process is carried out in controlled environments to reduce tungsten oxidation. After that, the molten ferrotungsten is tapped from the furnace, cast into molds, and cooled to create ingots or various shapes. To learn more about tungsten metal and ferrotungsten production, click here.
Sintering and Forming
Sintering is the process by which tungsten powder is transformed into pure tungsten metal and ferrotungsten. The powder is heated in a controlled environment in this stage to bind the particles together, generating a compressed mass. This mass is subsequently formed into the desired shape, which could be tungsten metal rods, sheets, wires, or specialized components.
Applications and final processing:
The formed tungsten metal or ferrotungsten is subjected to additional processing stages such as machining, polishing, and sometimes further alloying with other metals. The finished tungsten metal product has a wide range of applications, from manufacturing cutting tools and electrical contacts to aircraft, defense, and automobile components.
Understanding the process from tungsten ore to final product, including the provides a deeper appreciation for the versatility and adaptability of this outstanding metal. Tungsten metal and its alloys are projected to play a critical role in determining the future of technology and industry as the needs of key sectors and industries continue to evolve.