Are you curious about how 3D scanning technology works? Do you want to understand the mechanics behind capturing digital representations of real-life objects and environments?
This blog post will take you on a journey through the fascinating world of 3D scanning. From structured light scanners to laser triangulation systems, we’ll explore different approaches to capturing depth and detail in three dimensions.
So strap in and get ready for a deep dive into the cutting-edge world of 3D imaging!
Laser or Structured Light Scanning
Laser scanning, also known as structured light scanning, is a 3D scanning technology that uses a laser to create a 3D image of an object. The laser beam is projected onto the object and the reflections are captured by a camera. The camera is then able to create a 3D image of the object.
Structured light scanning is one of the most popular 3D scanning technologies because it is fast, accurate, and relatively easy to use. It can be used to scan objects of all shapes and sizes, and can even be used to scan people.
Point Cloud Data
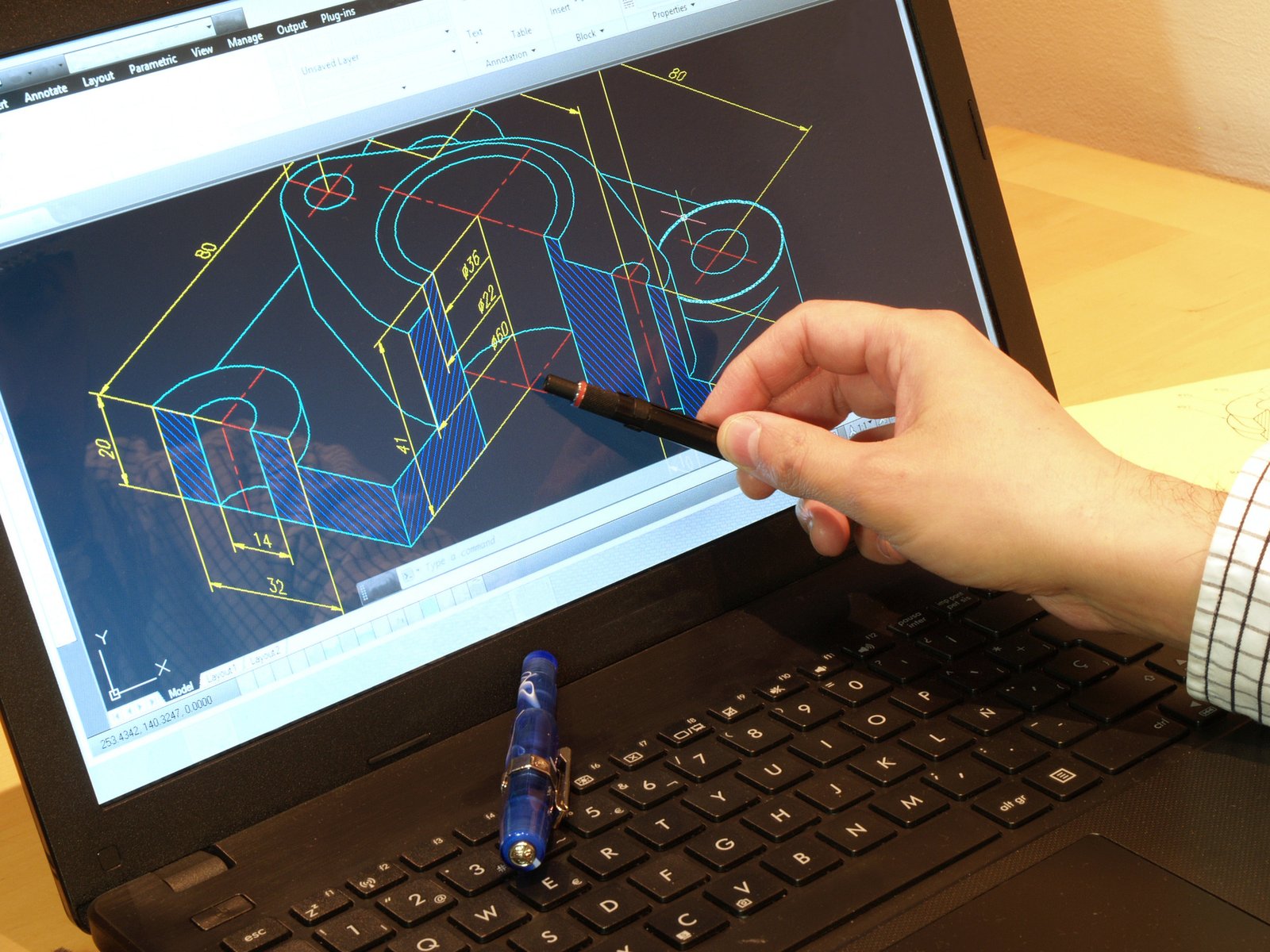
Point Cloud Data is the 3D data captured by a 3D scanner. This data is made up of points in space that are used to create a 3D model of an object or environment. This data can be used to create a variety of different types of models, including CAD models, BIM models, and point clouds.
Triangulation
The basic principle behind 3D scanning is called triangulation. Triangulation is the process of taking two-dimensional measurements and using them to calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of an object.
There are several ways to do this, but the most common method used in 3D scanning is laser triangulation. This involves shining a laser onto the object being scanned and then measuring the angle and distance of the reflected light with respect to the scanner. By knowing the angle and distance of the reflected light, it is possible to calculate the position of the point on the object that was hit by the laser.
Post-Processing
To generate a 3D model from the raw data captured by a 3D scanner, that data must first be processed. This is done through a process of algorithms and software that “clean up” the data and prepare it for 3D printing or other uses.
The specifics of this post-processing will vary depending on the type of 3D scanner being used, as well as the type of output desired:
- 3D printable file
- CAD model
- BIM
But the general steps start with the raw data that is converted into a mesh. Then, the mesh is cleaned up and repaired. And finally, the mesh is converted into the desired file format.
Each of these steps is important to create a high-quality 3D model from 3D scanning data. If any one of them is skipped or not done properly, it can result in a lower-quality model with inaccuracies or holes. To have quality results, you have to make sure to shop 3d scanners that are also of high quality.
Understand How the 3D Scanning Technology Works
3D scanning technology has become increasingly important in multiple industries as well as the private sector. This technology is rapidly revolutionizing the way we interact with the physical world.
From creating digital characters for CGI movies to 3D printing prosthetics, the potential applications of 3D scanning technology are virtually limitless. Try 3D scanning for yourself to experience the power and accuracy firsthand!
For more reads aside from technology trends or 3D technological advancements, visit our blog page.